In today’s fast-moving, data-driven world, businesses generate and rely on vast amounts of information to make better decisions, improve efficiency, and stay competitive. But not all data is the same—it comes in different forms, each with unique characteristics and challenges. Understanding these differences is key to storing, managing, and analyzing data effectively.
Broadly, data is classified into three main types: structured, unstructured, and semi-structured. Structured data is highly organized and stored in relational databases, making it easy to search and analyze. Unstructured data includes everything from emails and videos to social media posts, with no fixed format. Semi-structured data, like JSON and XML files, falls somewhere in between, containing some structure but not following a strict database format.
In this blog, we’ll explore these data types, their real-world applications, and best practices for managing them efficiently.
Table of Contents
- What is Data?
- Understanding Different Data Types: Making Sense of Your Business Information
- Data Storage & Management Strategies: Choosing the Right Approach
- Advantages & Challenges of Different Data Types: Choosing the Right Fit
- Applications of Each Data Type
- Advanced Technologies for Data Processing: How AI & Automation are Transforming Data Management
- The Future of Data Management: Key Trends & Best Practices
- Conclusion
What is Data?
Data is the backbone of modern businesses—it includes all the facts, figures, and insights companies collect during their daily operations. Whether it’s numbers, text, images, customer interactions, or sales records, data helps businesses make smarter decisions, understand customer needs, and improve their services.
The amount of data being generated is growing at an incredible rate. In 2020, the world produced over 64 zettabytes of data, and by 2025, this number is expected to exceed 180 zettabytes. This rapid increase is driven by the rise of digital devices, online platforms, and smart technologies.
For businesses, understanding and managing data is no longer optional—it’s essential. It helps identify trends, enhance customer satisfaction, and stay ahead of the competition. When used effectively, data can transform operations, boost efficiency, and drive better business outcomes.
Understanding Different Data Types: Making Sense of Your Business Information
Structured Data: Organized & Easily Searchable
Structured data is highly organized, making it easy to store, search, and analyze. Think of it as data neatly arranged in rows and columns, like an Excel spreadsheet or a database table. Because it follows a predefined schema, it maintains consistency and reliability.

Examples:
Customer Databases: Customer names, addresses, and purchase histories are stored in a database.
Financial Records: Transaction details, account balances, and other financial metrics maintained in accounting software.
Key Features:
Consistency: Data is uniform, making it straightforward to analyze.
Ease of Access: Due to its organized nature, retrieving specific information is quick and efficient.
Unstructured Data: Vast, Complex, & Harder to Analyze
Unlike structured data, unstructured data doesn’t follow a specific format. It includes free-form content like text, images, audio, and video, making it harder to store in traditional databases. Since it’s messy and diverse, advanced tools like machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) are often needed to analyze it.

Examples:
Emails: The content of emails varies greatly and doesn’t follow a set structure.
Social Media Posts: Comments, photos, and videos shared on platforms like Facebook or Instagram.
Multimedia Files: Images, videos, and audio recordings.
Key Features:
Diverse Formats: Comes in various forms, from text to multimedia.
Complex Analysis: Requires advanced tools and techniques, such as natural language processing (NLP) or machine learning, to extract meaningful insights.
Semi-Structured Data: The Best of Both Worlds
Semi-structured data sits between structured and unstructured data. It doesn’t follow a strict schema like structured data but contains tags, labels, or metadata that help organize it in a meaningful way.

Examples:
XML and JSON Files: Often used in web applications to transmit data.
Log Files: Records generated by software applications that, while not strictly structured, have a consistent format.
Key Features:
Flexibility: Allows for a more adaptable data model compared to strictly structured data.
Self-Describing: Contains metadata that provides context, making it easier to interpret.
No matter the size of your business, knowing how to handle structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data is key to effective data management. Whether you’re analyzing customer trends, managing digital content, or automating workflows, using the right approach for each data type can boost efficiency, improve decision-making, and drive business growth.
Now that you understand different data types, the next step is choosing the right enterprise search solution to manage them efficiently. Learn how to choose the best enterprise search solution for your business.
Key Differences Between Structured, Unstructured, and Semi-Structured Data
| Feature | Structured Data | Unstructured Data | Semi-Structured Data |
| Definition | Highly organized data stored in predefined schemas | Data that lacks a fixed format or structure | Data that contains tags/markers but no strict schema |
| Structure & Organization | Stored in tables with rows & columns | No fixed organization or format | Partially organized with flexible formats |
| Storage Methods | Relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server) | Object storage (Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage) | NoSQL databases (MongoDB, CouchDB, Cassandra) |
| Ease of Search & Retrieval | Easy to search & retrieve using SQL | Requires advanced tools like AI, NLP | Searchable but may require specialized tools |
| Ease of Analysis | Easily analyzed using structured queries (SQL) | Difficult to analyze without AI/ML techniques | Easier than unstructured data but requires parsing |
| Examples | CRM systems, financial records, inventory databases | Social media posts, videos, images, emails | JSON, XML, log files, sensor data |
| Data Processing Tools | SQL-based tools (Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server) | AI-based tools (NLP, deep learning, machine learning) | Big data tools (NoSQL, Hadoop, Spark) |
| Best Use Cases | Business intelligence, financial reporting | Customer sentiment analysis, multimedia processing | Web data exchanges, IoT applications, system logs |
| Challenges | Limited flexibility, requires a predefined schema | Hard to analyze, requires significant storage & processing power | Can be complex to manage and query efficiently |
Data Storage & Management Strategies: Choosing the Right Approach
Storing and managing data effectively is critical for businesses to ensure quick access, security, and efficient processing. Depending on the type of data—structured, unstructured, or semi-structured—different storage solutions and management strategies are required. Let’s explore the best practices for handling each.
Structured Data: Storing & Managing Organized Information
Structured data is highly organized, easy to search, and typically stored in relational databases. This makes it ideal for applications that require quick retrieval and well-defined schemas.
Common Storage Solutions:
- Relational Databases: These databases store data in tables with predefined schemas, making it straightforward to query and manage.
Examples:
- MySQL: An open-source relational database management system known for its reliability and ease of use.
- PostgreSQL: A powerful, open-source object-relational database system that offers advanced features.
- Microsoft SQL Server: A relational database management system developed by Microsoft, designed for various enterprise applications.
Management Strategies:
- Data Warehouses: Consider using data warehouses for large volumes of structured data. They allow for efficient storage and analysis and support complex queries and reporting.
Examples:
- Amazon Redshift: A fully managed data warehouse service in the cloud.
- Google BigQuery: Serverless, highly scalable, and cost-effective multi-cloud data warehouse.
- Snowflake: A cloud-based data warehousing platform that enables data storage, processing, and analytic solutions.
Unstructured Data: Managing Vast & Diverse Information
Unstructured data includes text, images, videos, emails, and social media content, which lack a predefined format and require specialized storage solutions.
Common Storage Solutions:
- Object Storage Services: These services manage data as objects, making them suitable for storing large amounts of unstructured data.
Examples:
- Amazon S3: A scalable storage solution that allows businesses to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time.
- Google Cloud Storage: Offers unified object storage for developers and enterprises, from live data serving to data analytics and machine learning.
- Azure Blob Storage: Microsoft’s object storage solution for the cloud, optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data.
Management Strategies:
- Data Lakes: Implementing a data lake can be beneficial for unstructured data. A data lake is a centralized repository that allows you to store all your structured and unstructured data at any scale. It enables you to run different types of analytics to guide better decisions.
Examples:
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2: Combines the power of a high-performance file system with massive scale and economy to help speed your time to insight.
- AWS Lake Formation: A service that makes setting up a secure data lake easy in days.
Semi-Structured Data: Balancing Flexibility & Organization
Semi-structured data contains elements of both structured and unstructured data, often stored in formats like JSON or XML.
Common Storage Solutions:
- NoSQL Databases: Designed to handle a wide variety of data models, including key-value, document, columnar, and graph formats, making them ideal for semi-structured data.
Examples:
- MongoDB: A document-oriented NoSQL database that uses JSON-like documents with optional schemas.
- CouchDB: A database that uses JSON for documents, JavaScript for MapReduce queries, and regular HTTP for its API.
- Cassandra: A highly scalable, high-performance distributed database designed to handle large amounts of data across many commodity servers.
Management Strategies:
- Flexible Schema Design: Leverage NoSQL databases’ flexible schema capabilities to accommodate evolving data structures without significant disruptions.
- Indexing: Implement indexing strategies to improve query performance, ensuring efficient data retrieval.
Cloud-Based Data Management: Scalable & Secure Solutions
Cloud storage has transformed data management, offering businesses scalability, cost savings, and remote accessibility.
Strategies:
- Assess Data Needs: Evaluate your data types and business requirements to choose appropriate cloud services.
- Implement Security Measures: To protect your data in the cloud, ensure data encryption, access controls, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor your cloud storage usage and performance, optimizing configurations to manage costs and maintain efficiency.
Implementing the right data storage and management strategy is key to optimizing search and boosting business ROI. Discover how enterprise search optimization can drive business growth.
Advantages & Challenges of Different Data Types: Choosing the Right Fit
Each type of data—structured, unstructured, and semi-structured—has its own strengths and challenges when it comes to storage, analysis, and scalability. Understanding these trade-offs helps businesses optimize data management strategies and choose the right approach for their needs.
Structured Data: Reliable & Easy to Analyze
Structured data is highly organized, making it ideal for databases and quick analysis. It follows a fixed format, ensuring consistency across business systems.
Advantages:
- Ease of Analysis: Structured data is organized in a predefined manner, making it straightforward to search and analyze using tools like SQL.
- Consistency: The uniform format ensures data is consistent across systems, facilitating reliable data management.
Challenges:
- Limited Flexibility: The rigid schema can make adapting to new data types or evolving business needs difficult.
- Scalability Issues: Managing and scaling structured databases can become resource-intensive as data volume grows.
Unstructured Data: Rich in Insights but Harder to Manage
Unstructured data includes text, images, videos, and emails, offering deep insights but requiring specialized tools for analysis.
Advantages:
- Rich Information: Unstructured data includes diverse formats, such as text, images, and videos, offering a wealth of information.
- Fast Accumulation: Since there’s no need for a predefined structure, unstructured data can be collected quickly from various sources.
Challenges:
- Complex Analysis: Extracting meaningful insights requires advanced tools and techniques like natural language processing or machine learning.
- Storage and Scalability: Managing large volumes of unstructured data can be challenging, often requiring significant storage and processing power.
Semi-Structured Data: The Best of Both Worlds
Semi-structured data sits between structured and unstructured data, offering some organization while maintaining flexibility.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Semi-structured data balances structure and flexibility, allowing for easier adaptation to changing data requirements.
- Ease of Integration: It can be more easily integrated into existing systems compared to unstructured data, facilitating data exchange and interoperability.
Challenges:
- Complex Management: Handling semi-structured data can be complex due to its varied formats and the need for appropriate parsing and storage solutions.
- Processing Overhead: Extracting and processing information may require additional computational resources and specialized tools.
No single data type is perfect for all use cases. Businesses must balance flexibility, scalability, and ease of analysis when choosing how to store, manage, and analyze their data. By understanding these advantages and challenges, businesses can leverage the right data strategies to drive smarter decisions and improve efficiency.
Real-Life Applications of Each Data Type
Understanding how to leverage structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data can give you a competitive edge. Let’s examine how these data types are used in real-life business scenarios.
Business Use Cases for Structured Data
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Structured data is like a well-organized file cabinet. It’s easy to sort and search, making it perfect for CRM systems. Businesses use structured data to store customer details such as names, contact information, purchase history, and preferences.
- Supply Chain Optimization:
Structured data in supply chains tracks inventory, shipments, and demand forecasts, enabling optimized stock levels, reduced waste, and predictive planning. Relational databases store this data efficiently, ensuring organized access for real-time decisions.
Business Use Cases for Unstructured Data
- Social Media Sentiment Analysis:
Unstructured data, such as social media posts, reviews, or customer feedback, contains valuable insights. Analyzing this data can help you understand customer opinions, trends, and sentiments toward your products or services.
- Fraud Detection in Finance:
Unstructured data can be a goldmine for identifying fraudulent activities in industries like banking and finance. By analyzing large amounts of transaction data and detecting patterns or anomalies, businesses can use AI and machine learning to spot suspicious behavior.
Business Use Cases for Semi-Structured Data
- Customer Feedback Processing:
Semi-structured data is often found in surveys, online reviews, or email responses. It may not follow a rigid structure, but it still has a specific format that makes it easier to analyze than entirely unstructured data. Businesses can use this data to extract key insights, such as customer satisfaction levels or suggestions for product improvements.
- IT Log File Analysis:
Semi-structured data also plays a big role in IT operations. Logs from servers, applications, and systems provide useful data that can be parsed and analyzed to monitor performance, detect security issues, and troubleshoot problems.
Advanced Technologies for Data Processing: How AI & Automation are Transforming Data Management
With data growing at an unprecedented rate, businesses need advanced technologies to process, analyze, and secure information efficiently. Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), ETL pipelines, and cybersecurity solutions play a key role in handling structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Here’s how these innovations are reshaping data management.
Machine Learning & AI for Smarter Data Processing
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are game-changers in data processing, helping businesses analyze massive datasets, detect patterns, and extract valuable insights.
- NLP for Unstructured Text Analysis:
Unstructured data, like customer feedback or social media posts, can be challenging to analyze manually. This is where Natural Language Processing (NLP) comes in. NLP allows machines to understand and interpret human language, making it easier to analyze large volumes of text.
For example, businesses can use NLP to track customer sentiment in social media or reviews, helping to improve products or services based on customer opinions.
- Deep Learning for Image and Video Recognition:
Another exciting AI application is deep learning, especially in image and video recognition. Deep learning algorithms can “train” on vast amounts of visual data, allowing machines to recognize patterns, objects, and even emotions in images or videos.
This is especially useful in industries like retail (e.g., visual product recognition) or security (e.g., surveillance cameras spotting suspicious activities).
- AI-Driven Analytics for Customer Insights:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing customer analytics. AI algorithms can sift through massive amounts of structured and unstructured data, detecting trends and patterns that would be hard for humans to spot.
For example, AI-driven analytics can help you understand customer behavior, predict future trends, and personalize marketing strategies to boost sales.
ETL Pipelines: Efficient Data Integration & Transformation
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) processes streamline data integration from multiple sources. These pipelines ensure that data is clean, structured, and ready for analysis.
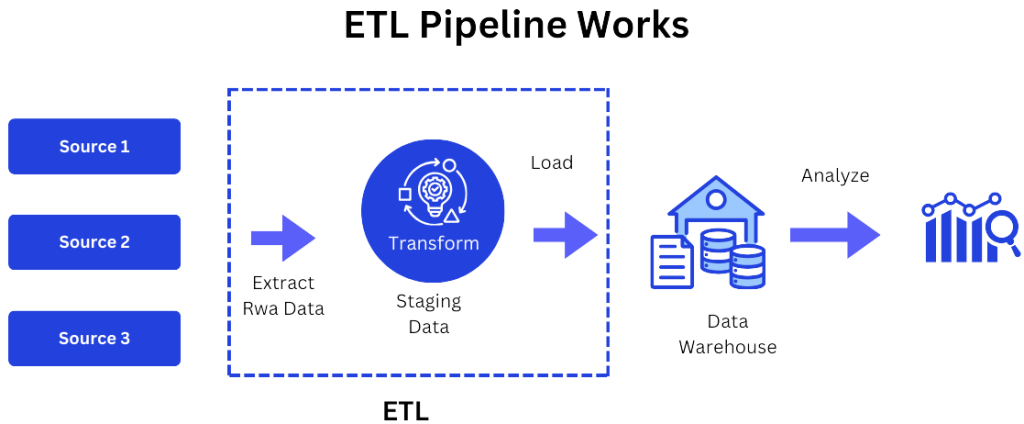
- ETL for Structured Data:
ETL is a process used to integrate structured data from different sources into a central data warehouse. First, data is extracted from various sources like databases, then transformed into a consistent format, and finally, loaded into a data warehouse for analysis. This makes structured data accessible and ready for reporting or decision-making.
- ELT for Semi-Structured and Unstructured Data:
Businesses often use ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) for semi-structured and unstructured data. Unlike ETL, the data is loaded into the system first and then transformed later. This approach is ideal for handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data, such as log files or social media posts, that may not fit neatly into traditional databases.
- Cloud-Based ETL Solutions for Scalability:
With cloud computing, businesses now have access to scalable ETL solutions. Cloud-based platforms allow you to process and integrate vast amounts of data with minimal upfront investment in infrastructure. This flexibility makes it easier to scale your data operations as your business grows and data volumes increase.
Cybersecurity Challenges & Solutions for Different Data Types
With data breaches on the rise, businesses must protect sensitive information across structured, unstructured, and semi-structured datasets.
- Structured Data: Database Encryption and Access Control
Structured data is often stored in relational databases, making it a common target for cyberattacks. Businesses use database encryption to protect this sensitive information, which converts data into an unreadable secure format without the proper decryption key.
- Unstructured Data: AI-Based Anomaly Detection
Unstructured data, such as social media posts or email communication, is more challenging to monitor for security threats. However, AI-based anomaly detection can help. By analyzing patterns in unstructured data, AI can identify unusual behavior and alert businesses in real time.
- Semi-Structured Data: Schema Validation and API Security
Semi-structured data, such as JSON or XML documents, requires careful validation to ensure data integrity. Businesses can use schema validation techniques to ensure the data is formatted correctly before processing.
Optimizing indexing and querying speed is essential for handling large datasets. Understand how Elasticsearch refresh intervals improve data processing.
The Future of Data Management: Key Trends & Best Practices
As data continues to grow exponentially, businesses must adapt to new technologies and best practices to store, manage, and analyze data efficiently. Emerging trends like hybrid cloud storage, AI-driven automation, and stronger security frameworks are shaping the future of data management. Here’s what businesses need to know to stay ahead in the data-driven era.
Trends in Data Storage & Processing
- Rise of Hybrid Cloud Storage Solutions:
In the future, more companies will turn to hybrid cloud storage. This means combining private and public clouds to store data. Hybrid solutions offer the flexibility to store sensitive data on private clouds while using public clouds for scalability and cost-efficiency.
- Automation in Data Classification and Tagging:
Automation is making data classification easier. Instead of manually tagging and organizing data, AI-powered tools automatically categorize and tag data, saving businesses time and reducing human error. This is especially useful when dealing with large volumes of unstructured data.
- AI-Powered Data Governance:
AI will play a big role in data governance. It will help businesses ensure data privacy, compliance, and security by automatically monitoring data access and use. AI will also help identify potential risks in real-time, allowing quicker action.
Best Practices for Businesses Handling Data
- Choosing the Right Storage Solutions for Different Data Types:
Businesses must pick the right storage solution for their data. Traditional databases work well for structured data, while cloud-based object storage is more suitable for unstructured data. Semi-structured data may benefit from NoSQL databases, which help businesses manage costs and improve efficiency.
- Implementing Strong Security and Compliance Frameworks:
As data regulations become stricter, businesses must focus more on security and compliance. Implementing robust encryption methods and access control systems is critical to protecting sensitive data.
- Leveraging AI for Automated Data Analysis:
AI will make data analysis faster and more accurate. Using AI tools, businesses can automatically analyze data, uncover insights, and make data-driven decisions without manual intervention.
Conclusion
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the differences between structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data is more than just technical knowledge—it’s a key driver of business success. Choosing the right data management strategy—whether it’s relational databases for structured data, object storage for unstructured data, or NoSQL solutions for semi-structured data—can streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and fuel business growth.
Beyond storage, leveraging AI-powered analytics, automation, and cloud-based solutions enables businesses to unlock valuable insights, improve decision-making, and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market. The key is to align your data strategy with your business goals, ensuring scalability, security, and long-term innovation.
By adopting smart data management practices, businesses can transform raw data into actionable intelligence, drive smarter decisions, and create a strong foundation for future success.

