Search engines are the gateway to the internet—the tools that help users navigate the vast ocean of online information. But how did they evolve into the powerful, AI-driven systems we rely on today? More importantly, why should businesses understand the mechanics of search?
In this blog, we will take a journey through the evolution of search engines, from the early days of basic keyword-based search to the advanced, algorithm-driven systems like Google that dominate today. By understanding how search works, businesses can optimize their websites, improve visibility, and attract more potential customers in an increasingly digital world.
Table of Contents
- The Rise of Early Search Engines
- Google’s Innovation and Its Impact
- Core Components of a Large-Scale Web Search Engine
- Evolution of Search Engine Technology: From Keywords to AI-Powered Search
- The Business Perspective: Why It Matters
- Conclusion
The Rise of Early Search Engines
In the early days of the internet, finding relevant information was a daunting task. There were no structured ways to navigate the growing number of websites, and users had to rely on web directories and primitive search engines.
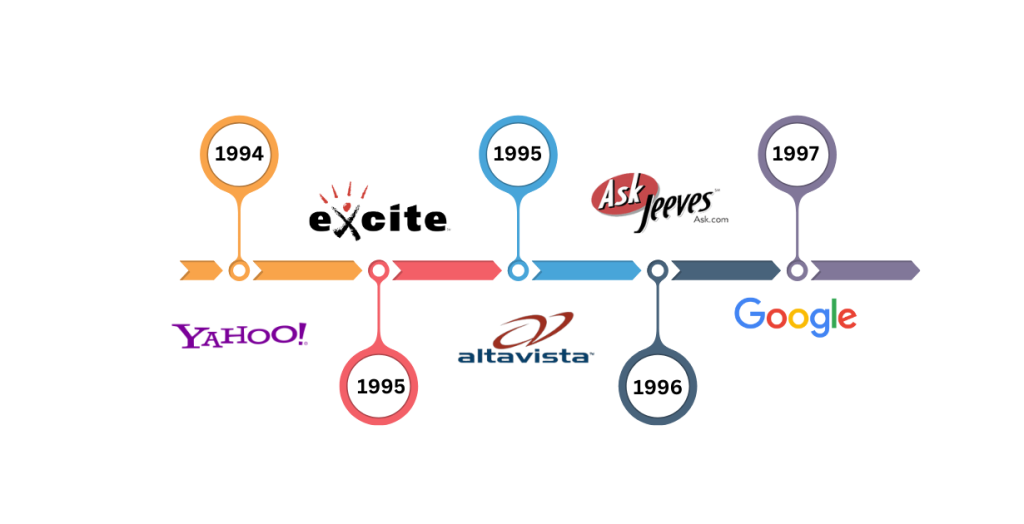
The First Search Engines: Simplicity with Major Limitations
The earliest search engines, including Archie (1990), Veronica, and Jughead, were designed to index FTP (File Transfer Protocol) archives rather than web pages. These tools were useful for locating files but were not full-fledged search engines as we know them today.
As the World Wide Web expanded, more advanced search engines like AltaVista, Lycos, and Yahoo! Search emerged. These engines worked by crawling web pages and indexing their content based on simple keyword matching. However, they had major shortcomings:
- No Understanding of Context: Searches were purely text-based—they didn’t consider the meaning behind queries.
- Low Relevance in Search Results: Websites could manipulate rankings by stuffing pages with repeated keywords.
- Manual Curation Required: Some early search engines relied on human editors to categorize websites, which was time-consuming and inconsistent.
Example: If a user searched for “best cameras,” these early search engines might return any page that contained the words ‘best’ and ‘cameras’, regardless of whether the content was relevant or not.
Although these search engines paved the way for information retrieval, they lacked the sophistication to understand intent, relevance, or quality—problems that Google would later address.
Google’s Innovation and Its Impact
The real revolution in search technology began when Larry Page and Sergey Brin introduced Google in 1998. Unlike its predecessors, Google was built on a groundbreaking algorithm known as PageRank, which transformed the way search engines ranked web pages.
How PageRank Changed Search Forever
Instead of ranking pages solely based on keyword matches, Google introduced a link-based ranking system. PageRank measured:
- The number of links pointing to a page (backlinks).
- The quality of those links (high-authority sites carried more weight).
- The interconnectedness of web pages, treating the internet like a network of recommendations.
Example: A webpage about “best DSLR cameras” with backlinks from trusted photography blogs, news websites, and manufacturers was considered more authoritative than a page with no references.
Google’s Ongoing Evolution
As search technology advanced, Google continued to refine its ranking methods by incorporating:
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: The RankBrain algorithm (introduced in 2015) helped Google understand user intent and interpret complex queries.
- Semantic Search: Instead of relying only on exact keyword matches, Google started understanding the meaning behind words, improving search accuracy.
- Mobile & Voice Search Optimization: With the rise of smartphones and voice assistants, Google adapted its search algorithms to provide better results for spoken and mobile queries.
By focusing on relevance, quality, and user experience, Google became the dominant search engine, handling billions of queries per day.
Why Understanding Search Engine Anatomy Matters for Businesses
For business owners, search engines are more than just information retrieval tools—they are a direct pathway to potential customers. A website that ranks higher on Google gets more visibility, clicks, and conversions than one buried in the search results.
Key Benefits of Understanding How Search Engines Work:
- Increased Website Visibility – Knowing how Google ranks pages helps businesses optimize their content and reach more users.
- Higher Search Rankings – Implementing SEO (Search Engine Optimization) best practices can push a website to the top of search results.
- Better User Experience – Google favors websites that load fast, are mobile-friendly, and offer valuable content—factors that also improve customer satisfaction.
- More Leads and Sales – Higher rankings = more website traffic = more potential customers.
The Business Impact of Search Optimization
Example 1: An e-commerce store selling sneakers that ranks on Page 1 of Google for “best running shoes” is far more likely to generate sales than a competitor ranking on Page 5.
Example 2: A local business (like a bakery or law firm) that optimizes its Google My Business profile and website content can appear in local search results, attracting nearby customers.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the core components of large-scale web search engines, trace the evolution of search technology, and highlight key innovations that have shaped the way we find information online.
Core Components of a Large-Scale Web Search Engine
A search engine is much more than just a tool that retrieves web pages. It consists of several essential components that work together to provide accurate and relevant search results.

Crawling & Indexing: Discovering and Storing Web Pages
Search engines start by crawling the web. This process involves automated bots, called web crawlers or spiders, visiting websites and gathering information. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, continuously expanding the search engine’s database.
Once a webpage is discovered, it goes through indexing. This means the search engine stores and organizes the page’s content in a massive database. The index allows quick retrieval of relevant pages when a user types in a search query. If a page is not indexed, it won’t appear in search results.
Large-scale web search engines share many indexing and crawling techniques with enterprise search systems. If you’re interested in how businesses can leverage these capabilities, read our detailed guide on Enterprise Search Services.
Ranking Algorithms: From PageRank to AI-Driven Models
After indexing, search engines use ranking algorithms to determine the order in which pages appear in search results. Google’s PageRank was the first major algorithm, ranking pages based on the number and quality of inbound links. Over time, ranking systems have evolved to include:
- Relevance of content to the user’s query.
- Mobile-friendliness and page loading speed.
- User engagement metrics such as click-through rates.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) to understand search intent.
Modern search engines use machine learning and AI-powered models, such as Google’s RankBrain, to improve ranking accuracy and deliver the most useful results.
Query Processing: Enhancing Search with NLP
When a user types a query, the search engine processes it to understand intent and meaning. This process has significantly improved with Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP allows search engines to:
- Interpret complex queries more effectively.
- Understand synonyms and context rather than just matching keywords.
- Provide direct answers instead of just a list of links.
With NLP advancements, search engines can handle voice search, predictive search, and conversational queries, making search results more intuitive and accurate.
Evolution of Search Engine Technology: From Keywords to AI-Powered Search
Search engines have come a long way from simple keyword-based lookups to AI-driven intelligent systems that understand user intent, predict queries, and even process images. Early search engines were limited to matching words with indexed content, often leading to irrelevant or low-quality results. Today, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning have made search engines smarter, faster, and more intuitive than ever.
Keyword-Based Search vs. Semantic Search
Originally, search engines relied on keyword-based searches, matching exact words in a query with indexed web pages. However, this method often led to poor results because it didn’t consider context or user intent.
With semantic search, engines now understand the meaning behind words. Using AI and machine learning, they analyze the intent behind queries, improving result accuracy. This shift has led to more relevant answers, even when users phrase questions differently.
Predictive Search & Voice Search: The AI-Powered Future
The way people search is changing. Predictive search anticipates user queries based on past searches and browsing behavior. This feature, seen in Google’s autocomplete suggestions, saves time and enhances user experience.
Meanwhile, voice search has gained popularity with smart assistants like Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa. Voice queries tend to be longer and more conversational, prompting search engines to improve their NLP capabilities.
Visual Search: Searching Beyond Text
Beyond text and voice, search engines now offer visual search, allowing users to search using images instead of words. Tools like Google Lens analyze images to identify objects, landmarks, and even translate text in real-time. This innovation is particularly valuable for e-commerce, helping users find products instantly by snapping a picture.
The Business Perspective: Why It Matters
For businesses, search engine visibility is a game-changer. The higher your website ranks, the more likely potential customers will discover your brand, leading to increased traffic, engagement, and conversions. However, search engines like Google are constantly evolving, meaning businesses must adapt their SEO strategies to stay relevant.
SEO & Search Ranking: Adapting to Google’s Evolving Algorithms
For businesses, ranking high on search engines is essential. Google’s ranking algorithms are constantly evolving, and staying updated with these changes can impact your website’s visibility. Implementing SEO best practices, such as using relevant keywords, optimizing site speed, and ensuring mobile-friendliness, can help improve your ranking.
Optimizing search performance isn’t just about web search—enterprise search optimization can also boost business efficiency. Learn more in our article on Revamp Your Business Growth with Enterprise Search Optimization for Better ROI.
User Experience & Engagement: The Importance of Speed & Structured Data
Search engines prioritize websites that offer a seamless user experience. This means ensuring fast-loading pages, mobile responsiveness, and structured data to help search engines understand content better. Sites that provide a positive user experience tend to rank higher and retain more visitors.
The Future of Search: AI-Powered Assistants, Conversational & Immersive Search
As AI and machine learning continue to advance, search is becoming more interactive. Voice search, chatbots, and AI-powered assistants are changing how users interact with search engines. Businesses that adopt AI-driven strategies, optimize for voice search, and embrace immersive search technologies, such as augmented reality (AR), will stay ahead in this evolving digital landscape.
Understanding how search engines operate and adapting your business strategies accordingly can help you maintain visibility and growth in the competitive online space. Next, we’ll discuss key takeaways and strategies to optimize your content for AI-driven search engines.
Conclusion
Search engines have evolved from basic keyword matchers to AI-driven, intent-based systems that power the internet today. Understanding their core structure, ranking algorithms, and technological advancements helps businesses and website owners optimize content, improve visibility, and stay competitive.
As search continues to embrace AI, voice, and visual search, businesses must adapt their SEO strategies and focus on user experience, structured data, and emerging trends. Those who keep up with search evolution will thrive in the digital landscape, ensuring their content remains discoverable, relevant, and impactful in the ever-changing world of search.

